ALMA Sees Super Stellar Nurseries at Heart of Sculptor Galaxy
Starburst galaxies transmute gas into new stars at a dizzying pace – up to 1,000 times faster than typical spiral galaxies like the Milky Way. To help understand why some galaxies "burst" while others do not, an international team of astronomers used the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) to dissect a cluster of star-forming clouds at the heart of NGC 253, one of the nearest starburst galaxies to the Milky Way.
"All stars form in dense clouds of dust and gas," said Adam Leroy, an astronomer formerly with the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) in Charlottesville, Virginia, and now with the Ohio State University (OSU) in Columbus. "Until now, however, scientists struggled to see exactly what was going on inside starburst galaxies that distinguished them from other star-forming regions."
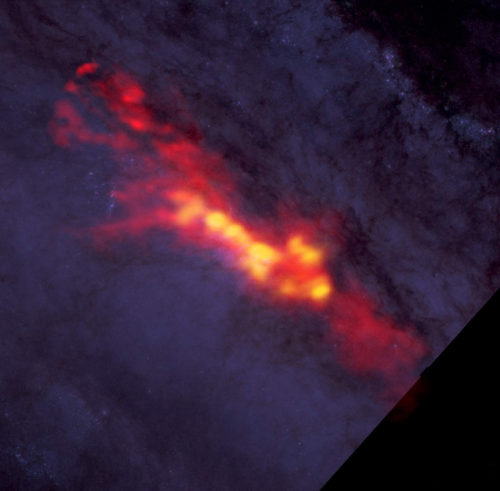
What is the recipe for starburst? Astronomers studied NGC 253 with ALMA to find out. These new ALMA data reveal a diffuse envelope of carbon monoxide gas (shown in red), which surrounds stellar nurseries -- regions of active star formation (in yellow). By dissecting these regions with ALMA, astronomers are uncovering clues to the processes and conditions that drive furious star formation. The ALMA data are superimposed on a Hubble image that covers part of the same region. Credit: B. Saxton (NRAO/AUI/NSF); ALMA (NRAO/ESO/NAOJ), A. Leroy; STScI/NASA, ST-ECF/ESA, CADC/NRC/CSA
ALMA changes that by offering the power to resolve individual star-forming structures, even in distant systems. As an early demonstration of this capability, Leroy and his colleagues mapped the distributions and motions of multiple molecules in clouds at the core of NGC 253, also known as the Sculptor Galaxy.
Sculptor, a disk-shape galaxy currently undergoing intense starburst, is located approximately 11.5 million light-years from Earth, which is remarkably nearby for such an energetic star factory. This proximity makes Sculptor an excellent target for detailed study.
"There is a class of galaxies and parts of galaxies, we call them starbursts, where we know that gas is just plain better at forming stars," noted Leroy. "To understand why, we took one of the nearest such regions and pulled it apart – layer by layer – to see what makes the gas in these places so much more efficient at star formation."
Animation of ALMA data reveals a diffuse envelope of carbon monoxide gas (shown in red), which surrounds stellar nurseries -- regions of active star formation (in yellow). By dissecting these regions with ALMA, astronomers are uncovering clues to the processes and conditions that drive furious star formation. The ALMA data are superimposed on a Hubble image that covers part of the same region. Credit: B. Saxton (NRAO/AUI/NSF); ALMA (NRAO/ESO/NAOJ), A. Leroy; STScI/NASA, ST-ECF/ESA, CADC/NRC/CSA
ALMA’s exceptional resolution and sensitivity allowed the researchers to first identifying ten distinct stellar nurseries inside the heart of Sculptor, something that was remarkably hard to accomplish before because earlier telescopes blurred the different regions together.
The team then mapped the distribution of about 40 millimeter-wavelength "signatures" from different molecules inside the center of the galaxy. This was critically important since different molecules correspond to different conditions in and around star-forming clouds. For example, carbon monoxide (CO) corresponds to massive envelopes of less dense gas that surround stellar nurseries. Other molecules, like hydrogen cyanide (HCN), reveal dense areas of active star formation. Still rarer molecules, like H13CN and H13CO+, indicate even denser regions.
By comparing the concentration, distribution, and motion of these molecules, the researchers were able to peel apart the star-forming clouds in Sculptor, revealing that they are much more massive, ten times denser, and far more turbulent than similar clouds in quiescent galaxies like the Milky Way.
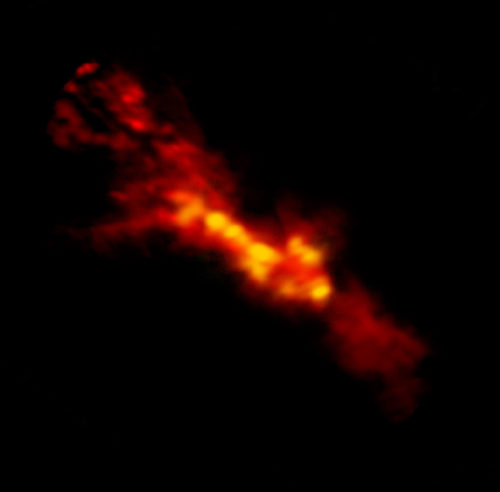
ALMA image of starbursting clouds inside NGC 253. The red region is the lower density CO gas surrounding higher density star-forming regions in yellow.Credit: B. Saxton (NRAO/AUI/NSF); ALMA (NRAO/ESO/NAOJ), A. Leroy
These stark differences suggest that it’s not just the number of stellar nurseries that sets the throttle for a galaxy to create new stars, but also what kind of stellar nurseries are present. Because the star-forming clouds in Sculptor pack so much material into such a small space, they are simply better at forming stars than the clouds in a galaxy like the Milky Way. Starburst galaxies, therefore, show real physical changes in the star-formation process, not just a one-to-one scaling of star formation with the available reservoir of material.
"These differences have wide-ranging implications for how galaxies grow and evolve," concluded Leroy. "What we would ultimately like to know is whether a starburst like Sculptor produces not just more stars, but different types of stars than a galaxy like the Milky Way. ALMA is bringing us much closer to that goal."
These results are accepted for publication in the Astrophysical Journal and are being presented February 15, 2015, at a news conference at the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) meeting in San Jose, California.
More information
The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), an international astronomy facility, is a partnership of the European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO), the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) and the National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS) of Japan in cooperation with the Republic of Chile. ALMA is funded by ESO on behalf of its Member States, by NSF in cooperation with the National Research Council of Canada (NRC) and the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) in Taiwan and by NINS in cooperation with the Academia Sinica (AS) in Taiwan and the Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (KASI).
ALMA construction and operations are led by ESO on behalf of its Member States; by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO), managed by Associated Universities, Inc. (AUI), on behalf of North America; and by the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ) on behalf of East Asia. The Joint ALMA Observatory (JAO) provides the unified leadership and management of the construction, commissioning and operation of ALMA.
Contact:
Nicolás Lira
Education and Public Outreach Assistant
Joint ALMA Observatory
Santiago, Chile
Tel: +56 2 467 6519
Cell: +56 9 9445 7726
Email: [email protected]
Charles E. Blue
Public Information Officer
National Radio Astronomy Observatory
Charlottesville, Virginia, USA
Tel: +1 434 296 0314
Cell: +1 434.242.9559
E-mail: [email protected]
Richard Hook
Public Information Officer, ESO
Garching bei München, Germany
Tel: +49 89 3200 6655
Cell: +49 151 1537 3591
Email: [email protected]
Masaaki Hiramatsu
Education and Public Outreach Officer, NAOJ Chile
Observatory Tokyo, Japan
Tel: +81 422 34 3630
E-mail: [email protected]


